By Barbara Thomas March 11, 2025
Payment processing is an essential aspect of any business that involves accepting payments from customers. Whether it’s an online store, a brick-and-mortar shop, or a service-based business, the ability to process payments efficiently and securely is crucial for success.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of payment processing, exploring the various components of the payment processing ecosystem, the different types of payment methods and their processing, the role of payment gateways, step-by-step guide to payment processing, security measures, challenges and risks, emerging trends, and frequently asked questions.
Understanding the Payment Processing Ecosystem
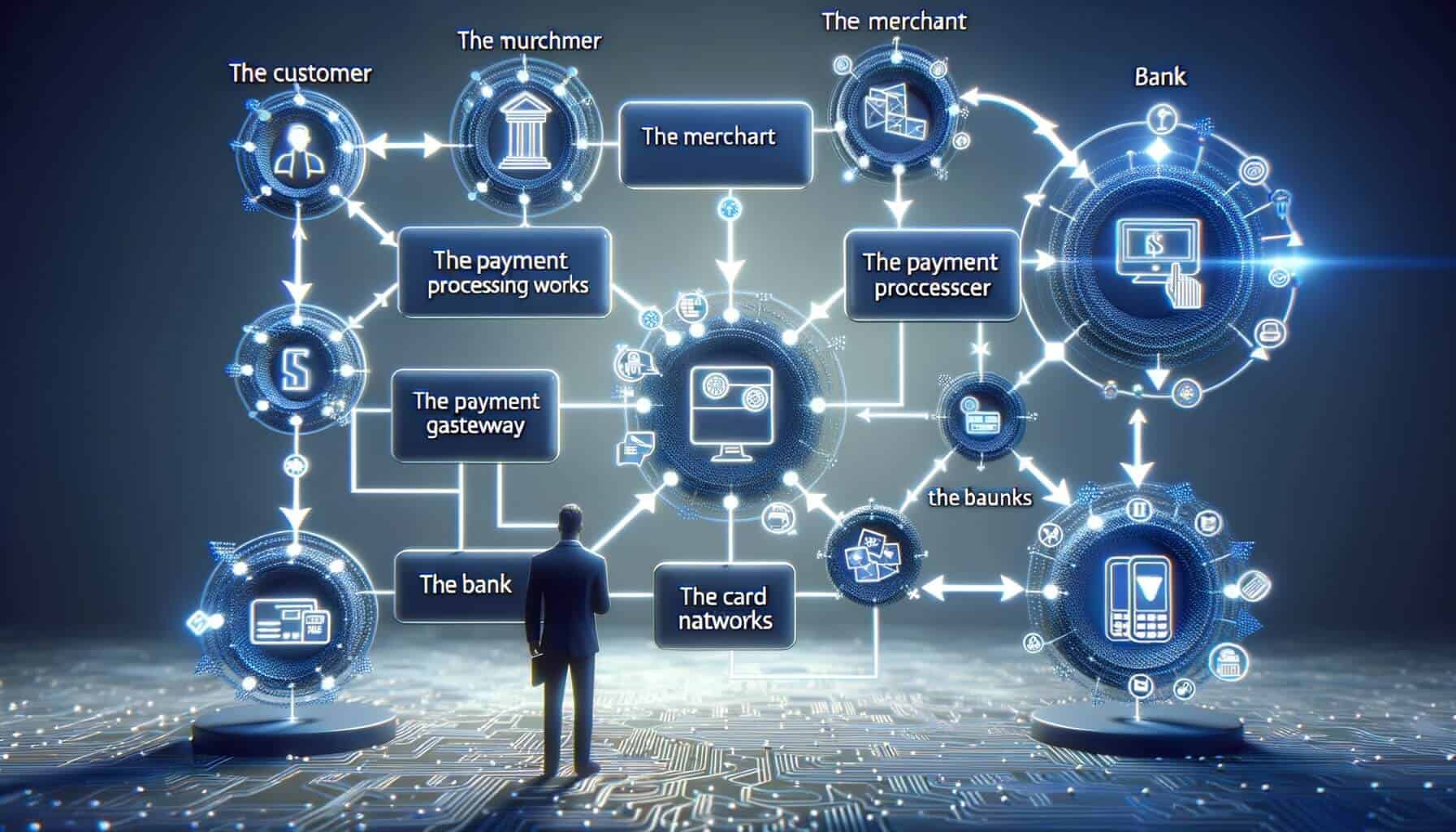
The payment processing ecosystem is a complex network of entities that work together to facilitate the movement of funds from the customer to the merchant. At its core, the ecosystem consists of the customer, the merchant, the acquiring bank, the issuing bank, and the payment processor. Let’s take a closer look at each of these entities and their roles in the payment processing ecosystem.
1. Customer: The customer is the individual or entity making a purchase and initiating the payment. They can use various payment methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, or bank transfers, depending on the options provided by the merchant.
2. Merchant: The merchant is the business or individual selling goods or services and receiving payments from customers. They must have a merchant account with an acquiring bank to accept payments.
3. Acquiring Bank: The acquiring bank, also known as the merchant bank, is a financial institution that provides merchant accounts to businesses. It acts as an intermediary between the merchant and the payment processor, facilitating the authorization and settlement of transactions.
4. Issuing Bank: The issuing bank is the financial institution that issued the customer’s payment card. It holds the customer’s funds and is responsible for authorizing or declining transactions based on the available balance and other factors.
5. Payment Processor: The payment processor is a third-party service provider that handles the technical aspects of payment processing. It connects the merchant’s payment gateway to the acquiring bank and facilitates the secure transmission of transaction data.
Types of Payment Methods and their Processing

There are various payment methods available to customers, each with its own processing requirements. Let’s explore some of the most common payment methods and how they are processed.
1. Credit Cards: Credit cards are a popular payment method that allows customers to make purchases on credit. When a customer makes a payment using a credit card, the payment processor sends the transaction details to the acquiring bank for authorization. If approved, the funds are transferred from the issuing bank to the acquiring bank, and the transaction is settled.
2. Debit Cards: Debit cards are linked to the customer’s bank account and allow for direct payment from available funds. The processing of debit card transactions is similar to credit cards, with the payment processor sending the transaction details to the acquiring bank for authorization. However, instead of transferring funds from the issuing bank, the payment processor deducts the amount from the customer’s bank account.
3. Mobile Wallets: Mobile wallets, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, have gained popularity in recent years. These wallets store the customer’s payment card information securely and allow for contactless payments using near-field communication (NFC) technology. When a customer makes a payment using a mobile wallet, the payment processor communicates with the wallet provider to authorize and process the transaction.
4. Bank Transfers: Bank transfers, also known as electronic funds transfers (EFT), involve the direct transfer of funds from the customer’s bank account to the merchant’s bank account. This payment method typically requires the customer to provide their bank account details, and the payment processor facilitates the secure transfer of funds between the banks.
The Role of Payment Gateways in Processing Transactions

Payment gateways play a crucial role in the payment processing ecosystem by securely transmitting transaction data between the customer, the merchant, and the payment processor. A payment gateway acts as a virtual point-of-sale terminal, encrypting sensitive payment information and facilitating the authorization and settlement of transactions. Let’s explore the key functions and features of payment gateways.
1. Encryption and Security: Payment gateways use encryption technology to protect sensitive payment data, such as credit card numbers, from unauthorized access. They employ secure socket layer (SSL) or transport layer security (TLS) protocols to encrypt the data during transmission, ensuring that it cannot be intercepted or tampered with.
2. Payment Data Storage: Payment gateways may offer the option to store customer payment data securely for future use. This feature, known as tokenization, replaces the sensitive payment information with a unique identifier called a token. The token can be used for subsequent transactions without exposing the actual payment data, reducing the risk of data breaches.
3. Payment Method Support: Payment gateways support various payment methods, allowing merchants to accept payments from customers using credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, and other payment options. They integrate with multiple payment processors and acquiring banks, providing flexibility and choice to merchants.
4. Fraud Prevention: Payment gateways employ advanced fraud detection and prevention mechanisms to protect merchants from fraudulent transactions. They analyze transaction data in real-time, using machine learning algorithms and rule-based systems to identify suspicious patterns and flag potentially fraudulent activities.
Step-by-Step Guide to Payment Processing
Now that we have a good understanding of the payment processing ecosystem and the role of payment gateways, let’s walk through the step-by-step process of payment processing.
1. Customer Initiates Payment: The customer selects the desired products or services and proceeds to the checkout page. They choose the preferred payment method and provide the necessary payment details, such as credit card number, expiration date, and CVV code.
2. Payment Gateway Transmits Data: The payment gateway securely transmits the payment data to the payment processor. It encrypts the data using SSL or TLS protocols to protect it from unauthorized access.
3. Payment Processor Sends Authorization Request: The payment processor receives the payment data from the payment gateway and sends an authorization request to the acquiring bank. The request includes the transaction details, such as the amount, payment method, and customer information.
4. Acquiring Bank Authorizes Transaction: The acquiring bank receives the authorization request from the payment processor and verifies the customer’s payment details. It checks the available balance, verifies the cardholder’s identity, and performs fraud checks. If the transaction is approved, the acquiring bank sends an authorization code to the payment processor.
5. Payment Processor Sends Approval to Payment Gateway: The payment processor receives the authorization code from the acquiring bank and sends it to the payment gateway. The payment gateway then displays a confirmation message to the customer, indicating that the payment was successful.
6. Merchant Processes Order: Upon receiving the payment confirmation, the merchant processes the customer’s order. They may generate an invoice, update inventory, and initiate the delivery of goods or services.
7. Settlement and Funds Transfer: At the end of the day or a specified settlement period, the acquiring bank initiates the settlement process. It transfers the funds from the customer’s issuing bank to the merchant’s acquiring bank. The acquiring bank deducts any applicable fees and deposits the remaining funds into the merchant’s bank account.
Security Measures in Payment Processing

Security is of paramount importance in payment processing to protect sensitive customer data and prevent fraudulent activities. Payment processors and payment gateways employ various security measures to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of payment transactions. Let’s explore some of the key security measures used in payment processing.
1. Encryption: Payment processors and gateways use encryption technology to encrypt payment data during transmission. SSL and TLS protocols are commonly used to establish a secure connection between the customer’s browser and the payment gateway, ensuring that the data cannot be intercepted or tampered with.
2. Tokenization: Tokenization is a technique used to replace sensitive payment data with a unique identifier called a token. Payment gateways may offer tokenization services, allowing merchants to store customer payment data securely. By using tokens instead of actual payment data, the risk of data breaches is significantly reduced.
3. PCI DSS Compliance: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder data. Payment processors and gateways must comply with PCI DSS requirements to ensure the secure handling of payment data. This includes maintaining a secure network, implementing strong access controls, regularly monitoring and testing systems, and maintaining an information security policy.
4. Fraud Detection and Prevention: Payment processors employ sophisticated fraud detection and prevention mechanisms to identify and mitigate fraudulent activities. They analyze transaction data in real-time, using machine learning algorithms and rule-based systems to detect suspicious patterns and flag potentially fraudulent transactions. Merchants can also implement additional fraud prevention measures, such as address verification and card security code checks.
Challenges and Risks in Payment Processing
While payment processing has become more streamlined and secure over the years, there are still challenges and risks that businesses must navigate. Let’s explore some of the common challenges and risks associated with payment processing.
1. Chargebacks: Chargebacks occur when a customer disputes a transaction and requests a refund from their issuing bank. Chargebacks can be costly for merchants, as they may result in the loss of revenue, additional fees, and damage to the merchant’s reputation. Merchants must have robust dispute resolution processes in place to handle chargebacks effectively.
2. Fraudulent Transactions: Fraudulent transactions pose a significant risk to merchants and payment processors. Fraudsters are constantly evolving their tactics, making it challenging to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. Merchants must implement robust fraud prevention measures and regularly monitor transactions for suspicious patterns.
3. Data Breaches: Data breaches can have severe consequences for businesses and their customers. A data breach can result in the theft of sensitive payment data, leading to financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Payment processors and gateways must have robust security measures in place to protect customer data and comply with data protection regulations.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Payment processing is subject to various compliance and regulatory requirements, such as PCI DSS, anti-money laundering (AML), and know your customer (KYC) regulations. Non-compliance can result in penalties, fines, and reputational damage. Businesses must stay up to date with the latest regulations and ensure that their payment processing practices are compliant.
Emerging Trends in Payment Processing
The payment processing landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. Let’s explore some of the emerging trends in payment processing that are shaping the future of the industry.
1. Contactless Payments: Contactless payments, enabled by technologies such as NFC and QR codes, are gaining popularity. Customers can make payments by simply tapping their payment card or scanning a QR code, eliminating the need for physical contact with payment terminals. Contactless payments offer convenience, speed, and enhanced security.
2. Mobile Payments: With the widespread adoption of smartphones, mobile payments are becoming increasingly popular. Mobile wallets, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, allow customers to make payments using their smartphones, eliminating the need for physical payment cards. Mobile payments offer convenience, seamless integration with other mobile services, and enhanced security features.
3. Biometric Authentication: Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, is being integrated into payment processing systems. Biometric authentication provides an additional layer of security, ensuring that only authorized individuals can initiate payments. It offers convenience and eliminates the need for passwords or PINs.
4. Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are disrupting the traditional payment processing landscape. Blockchain offers secure and transparent transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing trust. Cryptocurrencies provide an alternative payment method, enabling fast and low-cost cross-border transactions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Payment Processing
Q1. What is payment processing?
Answer: Payment processing refers to the handling of payment transactions between the customer and the merchant. It involves the authorization, settlement, and transfer of funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
Q2. What are the different types of payment methods?
Answer: The different types of payment methods include credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, bank transfers, and alternative payment methods such as PayPal and Venmo.
Q3. What is a payment gateway?
Answer: A payment gateway is a service that securely transmits transaction data between the customer, the merchant, and the payment processor. It encrypts sensitive payment information and facilitates the authorization and settlement of transactions.
Q4. How long does payment processing take?
Answer: The time taken for payment processing depends on various factors, such as the payment method used, the acquiring bank’s processing time, and the settlement period. In general, credit card transactions are authorized within seconds, while bank transfers may take a few business days to settle.
Q5. How can merchants protect against fraud in payment processing?
Answer: Merchants can protect against fraud by implementing robust fraud prevention measures, such as address verification, card security code checks, and transaction monitoring. They can also use fraud detection tools provided by payment processors and gateways.
Conclusion
Payment processing is a critical aspect of any business that accepts payments from customers. Understanding the payment processing ecosystem, the different types of payment methods, the role of payment gateways, and the step-by-step process of payment processing is essential for businesses to ensure smooth and secure transactions.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations in payment processing. Contactless payments, mobile payments, biometric authentication, and blockchain technology are some of the emerging trends that are shaping the future of payment processing. Businesses must stay abreast of these trends and adapt their payment processing strategies to meet the evolving needs and preferences of customers.
In conclusion, payment processing plays a vital role in the success of businesses, enabling them to accept payments efficiently and securely. By understanding the intricacies of payment processing and implementing robust security measures, businesses can provide a seamless payment experience for their customers while mitigating risks and staying ahead of the competition.